The quest for eternal youth is as old as time. While there may not be a magical elixir that can reverse aging, one proven solution does exist: exercise. The relationship between physical activity and aging has been extensively studied, and the results are clear—regular exercise can help you stay youthful, vibrant, and healthy for years to come. Whether it’s boosting your energy, improving cognitive function, or maintaining youthful skin, exercise truly is the key to a longer, healthier, and more youthful life.
Why Exercise is Essential for Youthful Vitality
As we age, our bodies go through numerous changes, from decreased muscle mass to slower metabolism and reduced cognitive function. These changes, while natural, are often accelerated by a sedentary lifestyle. Exercise works as a powerful tool to counteract these effects, keeping both the body and mind in peak condition.
1. Slows Down Physical Aging
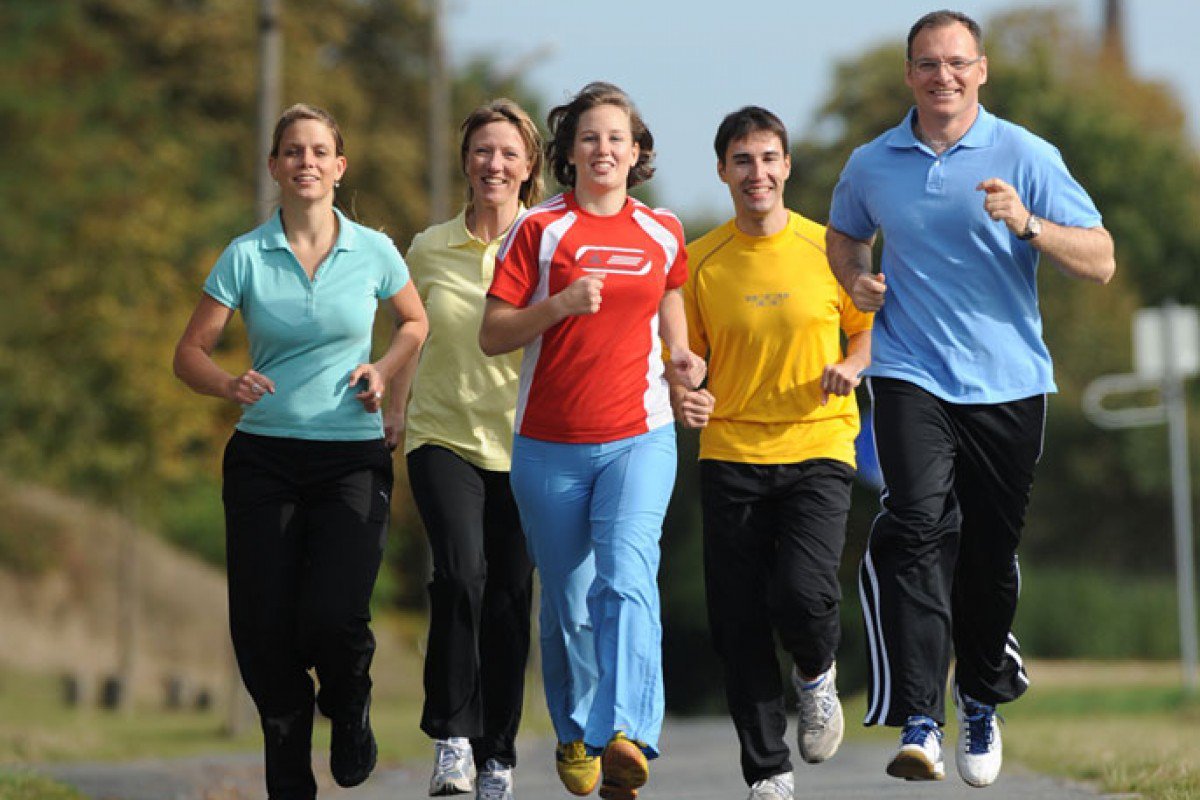
Exercise promotes overall physical health by improving cardiovascular function, increasing muscle mass, and boosting flexibility. Studies show that regular physical activity helps maintain bone density, prevents muscle atrophy, and encourages joint flexibility, all of which are critical in keeping the body youthful and agile as we age.
• Increased muscle strength: Strength training exercises are particularly effective in combating the natural decline of muscle mass and bone density that comes with aging.
• Boosted cardiovascular health: Aerobic exercises, such as running, cycling, and swimming, improve heart health, reduce blood pressure, and enhance circulation, which helps the body deliver nutrients more efficiently to maintain overall vitality.
2. Promotes Radiant, Youthful Skin
Your skin is one of the most visible markers of aging, and exercise can help maintain its youthful glow. Increased blood circulation from exercise brings more oxygen and nutrients to the skin, which can help repair damage and stimulate collagen production. Collagen is the protein responsible for skin elasticity, preventing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. In short, regular exercise can keep your skin looking fresh, firm, and youthful.
3. Boosts Cognitive Function
The brain, like any other organ, benefits from regular exercise. Physical activity increases the production of certain chemicals in the brain that improve mood, memory, and cognitive function. Studies have shown that regular aerobic exercise can increase the size of the hippocampus, the part of the brain responsible for memory and learning, which tends to shrink with age.
Incorporating exercise into your daily routine may not only delay cognitive decline but can also protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
4. Improves Mental Health and Reduces Stress
Stress and mental health issues are major contributors to aging. Chronic stress leads to increased levels of cortisol, a hormone that accelerates the aging process by breaking down collagen and contributing to inflammation. Exercise is a natural way to reduce stress, lower cortisol levels, and boost endorphins, the brain’s feel-good chemicals.
• Mood enhancement: Physical activity has been shown to decrease symptoms of anxiety and depression, leading to a more positive outlook on life—an essential ingredient for feeling young at heart.
• Stress reduction: Activities like yoga and Pilates not only strengthen the body but also teach mindfulness and relaxation techniques that help reduce stress and promote emotional well-being.
5. Supports Longevity and Disease Prevention
Research has consistently shown that individuals who engage in regular physical activity are at a reduced risk for chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Exercise strengthens the immune system, making it more efficient at warding off illness and infection.
Additionally, regular exercise lowers inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are known contributors to aging and many age-related diseases. People who engage in consistent physical activity have longer telomeres—the protective caps on the ends of chromosomes that naturally shorten with age. Longer telomeres are associated with a slower aging process and longer lifespan.
Types of Exercise to Keep You Youthful
It’s important to incorporate a balanced variety of exercises into your routine to fully reap the anti-aging benefits. Here are some types of exercises that are particularly effective in promoting youthfulness:
1. Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercises like walking, running, swimming, and cycling improve cardiovascular health and increase oxygen flow throughout the body. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week for maximum benefits. Aerobic exercise is also a powerful way to boost metabolism, helping to maintain a healthy weight and reducing fat accumulation that often comes with aging.
2. Strength Training
Strength or resistance training is key to maintaining muscle mass and bone density, which naturally decline as we age. Incorporating exercises like weightlifting, resistance bands, and bodyweight exercises (e.g., squats, lunges, push-ups) at least two to three times per week can help maintain a toned, youthful physique.
3. Flexibility and Balance Exercises
As we age, our flexibility and balance tend to decline, increasing the risk of falls and injuries. Yoga, Pilates, and tai chi are excellent ways to improve flexibility, balance, and posture. These exercises focus on controlled movements and mindfulness, enhancing both physical and mental well-being.
4. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by periods of rest or low-intensity activity. Studies show that HIIT can increase mitochondrial capacity (the powerhouse of cells), which tends to decline with age. This type of training improves endurance, cardiovascular health, and fat loss, making it a potent anti-aging exercise routine.
Creating an Exercise Routine for Youthful Aging
When designing a workout plan to promote youthfulness, it’s important to strike a balance between different types of exercises to target multiple aspects of health. Here’s a sample weekly routine:
• Monday: 30-minute brisk walk or light jog (aerobic exercise)
• Tuesday: Strength training focusing on upper body (push-ups, dumbbell curls, planks)
• Wednesday: Yoga or Pilates for flexibility and balance
• Thursday: High-intensity interval training (HIIT) session (20 minutes)
• Friday: Strength training focusing on lower body (squats, lunges, resistance bands)
• Saturday: 45-minute swim or bike ride (aerobic exercise)
• Sunday: Rest day with light stretching or meditation
Staying Motivated: Making Exercise a Lifelong Habit
Staying youthful through exercise requires long-term commitment, but it doesn’t have to be a chore. Here are some tips for staying motivated:
• Find activities you enjoy: Whether it’s dancing, hiking, or swimming, finding a form of exercise that you genuinely enjoy will make it easier to stick to your routine.
• Set realistic goals: Start small and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Setting achievable goals will help you stay motivated and prevent burnout.
• Exercise with a friend or group: Social support can make exercise more fun and keep you accountable.
• Celebrate progress: Keep track of your improvements in strength, endurance, and flexibility. Celebrating small milestones can help keep you motivated.
Conclusion: The True Fountain of Youth
In conclusion, while aging is inevitable, the decline in vitality and health that often accompanies it is not. Exercise is one of the most powerful tools we have to maintain a youthful appearance, energy levels, and mental sharpness. By staying physically active, we can not only improve the quality of our lives but also extend our healthspan—the period of life spent in good health. So, if you’re looking for the true fountain of youth, look no further than your local gym, park, or yoga mat.
References:
1. Harvard Health Publishing – The Anti-Aging Benefits of Exercise
2. Mayo Clinic – Exercise: 7 Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
3. Johns Hopkins Medicine – How Exercise Improves Your Physical and Mental Health