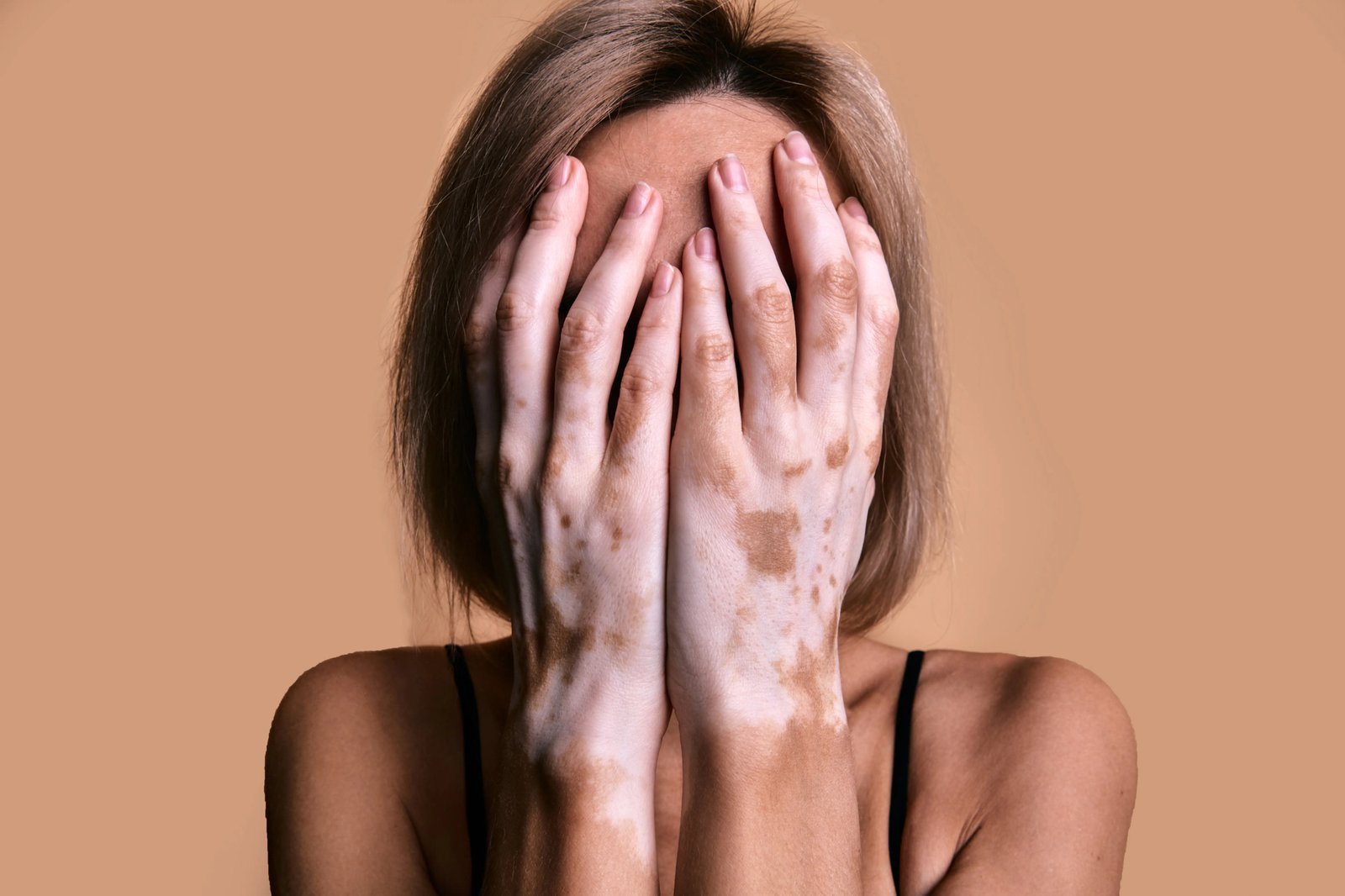
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition that results in the loss of pigmentation in patches of the skin. It affects millions of people worldwide, causing both physical and emotional challenges. In this article, we explore the causes of vitiligo, its symptoms, and the latest treatment options to help manage and improve this condition.
What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing pigment in the skin. As these cells are destroyed, white patches appear on the skin, typically starting on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, and arms.
Vitiligo can develop at any age but is most commonly seen in individuals under 30. While it is not contagious or life-threatening, it can significantly affect a person’s quality of life and self-esteem.
Causes of Vitiligo
The exact cause of vitiligo remains unclear, but several factors contribute to its development. These include:
- Autoimmune response: The immune system may mistakenly attack and destroy melanocytes, leading to loss of pigment.
- Genetics: There is evidence suggesting that vitiligo can run in families. People with a family history of autoimmune diseases are at a higher risk.
- Environmental triggers: Stress, sunburn, or exposure to industrial chemicals may contribute to the onset of vitiligo.
- Neurogenic factors: Some researchers believe that the nerves in the skin may release toxic substances that damage melanocytes.
Symptoms of Vitiligo
The most noticeable symptom of vitiligo is the appearance of white or depigmented patches on the skin. These patches can appear anywhere but are most common on areas exposed to the sun. Additional symptoms may include:

- Rapid pigmentation loss: The initial patch may spread quickly to other areas of the body.
- Hair depigmentation: Hair in the affected areas, such as on the scalp or eyebrows, may turn white or gray.
- Premature graying: Some individuals may notice early graying of the hair, eyelashes, or beard.
Vitiligo is often classified into two types:
- Segmental vitiligo: This type affects one side or part of the body and is more common in younger individuals.
- Non-segmental vitiligo: This is the more common form, where depigmentation occurs symmetrically on both sides of the body.

Treatment Options for Vitiligo
While there is no cure for vitiligo, several treatments are available to help restore pigmentation or minimize the appearance of depigmented patches. Treatment plans depend on the extent of the condition and the individual’s preferences.
- Topical Corticosteroids: Corticosteroid creams are often the first line of treatment for small, localized areas of vitiligo. These creams can help return color to the skin by reducing inflammation and slowing the spread of depigmentation. Early treatment typically yields the best results.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: For patients with facial vitiligo or sensitive areas, calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus may be prescribed. These medications work by suppressing the immune response, reducing the destruction of melanocytes.
- Phototherapy (UV Light Treatment): Narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) therapy is a widely used treatment for vitiligo, especially for those with widespread depigmentation. Exposure to UVB light can stimulate melanocyte activity and promote repigmentation. Phototherapy is usually done two to three times a week under medical supervision.
- Excimer Laser: This targeted laser therapy is an effective treatment for small, localized patches of vitiligo. The excimer laser emits UVB light, which helps to stimulate repigmentation in specific areas.
- Surgical Options: For individuals with stable vitiligo that has not progressed in several years, surgical procedures such as skin grafting or melanocyte transplantation may be considered. These surgeries aim to restore pigment to depigmented areas by transplanting healthy skin or melanocytes.
- Depigmentation Therapy: In cases where vitiligo affects more than 50% of the body, depigmentation therapy may be recommended to even out the skin tone. This treatment involves using a depigmenting agent to lighten the remaining pigmented areas, resulting in a more uniform appearance.
- Camouflage Makeup: While not a medical treatment, many individuals with vitiligo use camouflage makeup to cover depigmented patches. Waterproof makeup products designed for vitiligo can blend with natural skin tones and provide psychological relief by improving appearance.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with vitiligo can be challenging, especially for individuals who experience social stigma or emotional distress due to the appearance of their skin. Support groups, counseling, and therapy can be beneficial for managing the psychological effects of vitiligo. Some patients find that speaking with others who share their experiences helps build confidence and resilience.
Managing Vitiligo: Tips for Daily Life
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes can help manage vitiligo and protect the skin. Here are some tips for those with vitiligo:
- Sun protection: Always use sunscreen with a high SPF to protect depigmented areas from sunburn, as they are more sensitive to UV radiation.
- Moisturize regularly: Keeping the skin moisturized can prevent dryness and irritation, which may worsen the appearance of vitiligo.
- Consider mental health support: Seek out emotional and psychological support if you find it difficult to cope with the social or emotional aspects of vitiligo.
Conclusion
Vitiligo is a complex and often misunderstood skin condition, but with the right treatment and support, individuals can manage its physical and emotional effects. While there is no cure for vitiligo, treatments like topical medications, phototherapy, and surgery offer hope for repigmentation and improved skin appearance. If you or someone you know is living with vitiligo, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to explore the best treatment options for your specific case.
References
- Mayo Clinic. “Vitiligo: Symptoms and Causes.” Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vitiligo/symptoms-causes/syc-20355912
- American Academy of Dermatology. “Vitiligo: Diagnosis and Treatment.” Available at: https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/vitiligo-treatment
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS). “Vitiligo.” Available at: https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/vitiligo
This article highlights the causes and treatments for vitiligo, providing individuals with insights into how to manage this condition and improve their quality of life.