Understanding Hemorrhoids: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Hemorrhoids, commonly known as piles, are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus that can cause discomfort, itching, and bleeding. Although they are often painful, hemorrhoids are typically treatable with lifestyle changes, over-the-counter medications, and in some cases, medical procedures. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, and most effective treatment options for hemorrhoids.
What Are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. They occur when the veins around the rectum or anus become inflamed or swollen, often due to increased pressure. There are two types of hemorrhoids:
- Internal hemorrhoids: Located inside the rectum, these are usually painless but can cause bleeding during bowel movements.
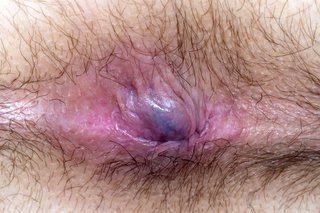
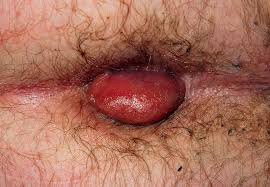
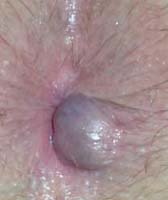
- External hemorrhoids: Found under the skin around the anus, these are more painful and can cause itching, irritation, and swelling.
In more severe cases, hemorrhoids can become thrombosed, meaning a blood clot forms inside the swollen vein, causing extreme pain and inflammation.
Causes of Hemorrhoids
Several factors can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids. The most common causes include:
- Straining during bowel movements: Excessive straining can increase pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus.
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea: Both conditions can lead to prolonged straining and irritation of the rectal veins.
- Pregnancy: The pressure of the growing uterus on the pelvic veins during pregnancy can increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
- Prolonged sitting: Sitting for extended periods, especially on the toilet, can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins in the lower body, increasing the likelihood of hemorrhoids.
- Low-fiber diet: A diet low in fiber can cause constipation, leading to straining and the development of hemorrhoids.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoid symptoms can vary depending on whether they are internal or external. Common symptoms include:
- Bleeding during bowel movements: Bright red blood may appear on toilet paper or in the toilet.
- Itching and irritation: Hemorrhoids can cause discomfort and itching around the anus.
- Pain and discomfort: External hemorrhoids, especially when thrombosed, can be very painful.
- Swelling around the anus: External hemorrhoids may cause visible swelling and lumps.
- A lump near the anus: This may be a thrombosed hemorrhoid, which is hard and painful to touch.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids
While hemorrhoids can be uncomfortable, they are usually treatable with home remedies and medical interventions. Here are some of the most effective treatments for hemorrhoids:
- Lifestyle and Dietary Changes The first step in treating hemorrhoids is to make simple lifestyle adjustments:
- Increase fiber intake: A high-fiber diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help soften stools and prevent constipation.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep stools soft and easier to pass.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity can prevent constipation and reduce pressure on the veins.
- Avoid prolonged sitting: Taking regular breaks from sitting can help reduce pressure on the rectal veins.
- Over-the-Counter Medications Several over-the-counter (OTC) treatments can relieve hemorrhoid symptoms:
- Topical creams and ointments: Products containing hydrocortisone or witch hazel can reduce itching, swelling, and pain.
- Stool softeners: These help prevent straining during bowel movements by making stools easier to pass.
- Pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Warm Sitz Baths Soaking the affected area in warm water for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, can soothe irritation and reduce swelling. Sitz baths are especially effective after bowel movements.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures If home treatments are ineffective, a doctor may recommend minimally invasive procedures, including:
- Rubber band ligation: A rubber band is placed around the base of an internal hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply, causing it to shrink and fall off.
- Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is injected into the hemorrhoid to shrink it.
- Coagulation therapy: A laser or infrared light is used to harden and shrink the hemorrhoid.
- Surgical Options In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary:
- Hemorrhoidectomy: The complete removal of large or thrombosed hemorrhoids. This procedure is highly effective but may require a longer recovery time.
- Hemorrhoid stapling: This procedure involves using a stapling device to block blood flow to the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink.
Preventing Hemorrhoids
Prevention is key when it comes to hemorrhoids. Simple lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids or prevent existing ones from worsening:
- Maintain a high-fiber diet: Eating plenty of fiber-rich foods can help prevent constipation and reduce the strain during bowel movements.
- Drink plenty of fluids: Staying hydrated helps keep stools soft and prevents constipation.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can promote healthy bowel function and reduce pressure on the veins.
- Avoid straining: Straining during bowel movements puts excess pressure on the rectal veins, leading to hemorrhoids.
Conclusion
Hemorrhoids are a common yet treatable condition that affects millions of people. By understanding the causes and symptoms, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage hemorrhoids effectively. From lifestyle changes and over-the-counter treatments to medical interventions, there are a variety of treatment options available to help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. If you are experiencing symptoms of hemorrhoids, consult a healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan.
References
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). “Hemorrhoids.” Available at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/hemorrhoids
- Mayo Clinic. “Hemorrhoids.” Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hemorrhoids/symptoms-causes/syc-20360268
- American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS). “Hemorrhoids.” Available at: https://fascrs.org/patients/disease-condition/hemorrhoids
This article outlines the causes, symptoms, and treatments of hemorrhoids, providing readers with actionable advice to manage this condition effectively.