Warts are one of the most common skin conditions affecting individuals of all ages. These small, rough growths can appear on various parts of the body, causing both physical discomfort and emotional stress due to their appearance. But what exactly causes warts, and how can they be prevented or treated? In this article, we dive into the viral origins of warts, explain how they spread, and discuss the best ways to manage them. Whether you’ve experienced warts firsthand or are simply curious, this comprehensive guide will provide you with all the information you need.
What Are Warts?
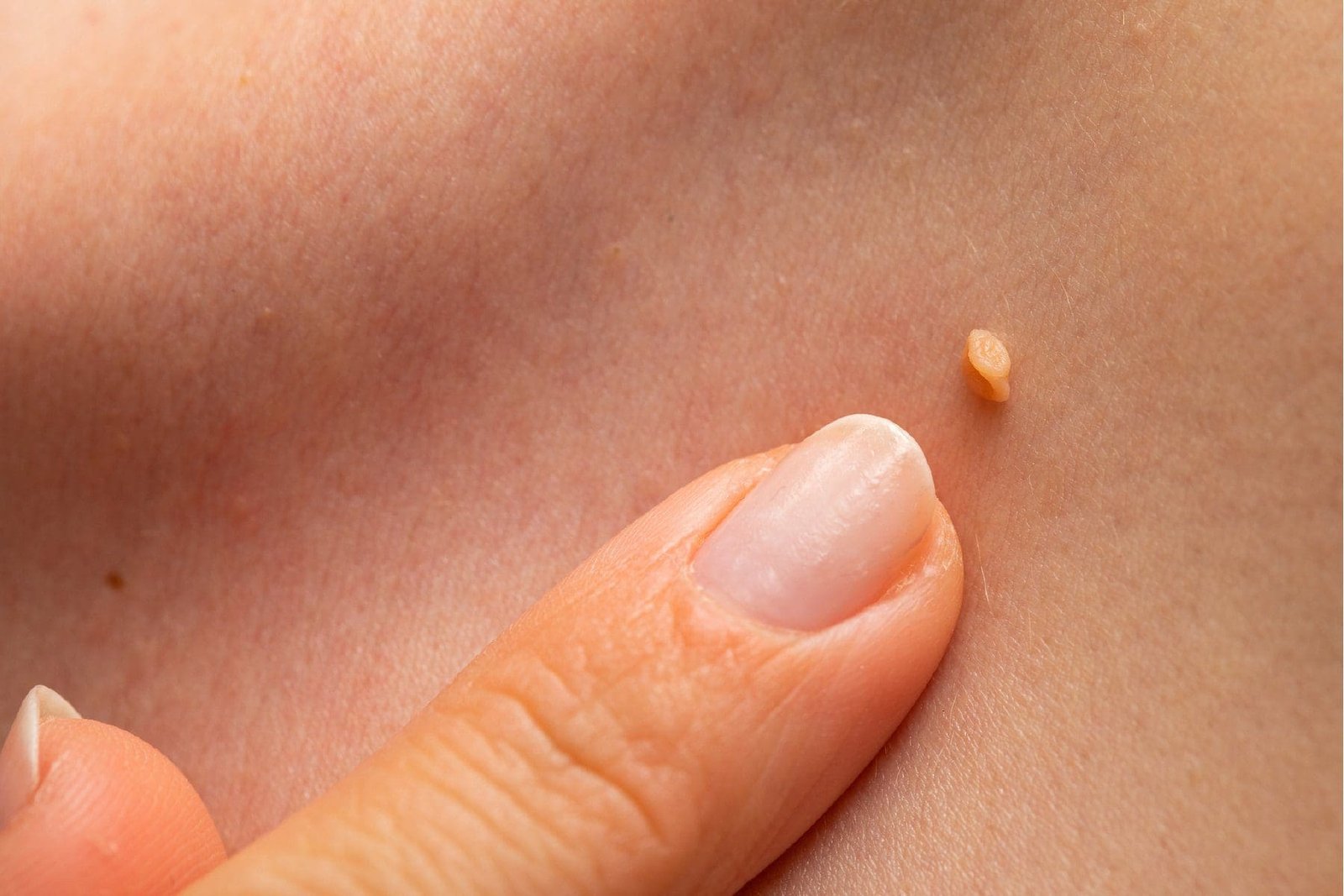
Warts are benign skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They are typically small, rough, and skin-colored, but their appearance can vary depending on the type of wart and its location on the body. Common warts are usually found on the hands, but they can also develop on the feet (plantar warts), face, or even genital areas.
How Do Warts Form?
Warts form when the HPV virus infects the top layer of the skin. The virus enters through small cuts or breaks in the skin, causing cells in the epidermis to grow rapidly, leading to the formation of a wart. While the HPV virus has more than 150 different strains, only a few of these strains are responsible for causing warts on the skin. Genital warts, for example, are caused by specific strains of HPV, which differ from those that cause common warts.
Types of Warts
There are several types of warts, each associated with specific HPV strains and characteristics. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
- Common Warts (Verruca Vulgaris)
These typically appear on the hands and fingers and are rough to the touch. They are caused by HPV types 1, 2, and 4. - Plantar Warts
Found on the soles of the feet, plantar warts can cause significant discomfort, particularly when walking. They grow inward due to the pressure from standing and are often surrounded by hardened skin. HPV types 1, 2, and 4 are the most common culprits. - Flat Warts (Verruca Plana)
These warts are smoother and smaller than common warts and often appear in clusters on the face, neck, or hands. HPV types 3, 10, and 28 are typically responsible for flat warts. - Genital Warts
These are sexually transmitted and appear on the genital and anal areas. HPV types 6 and 11 are most frequently associated with genital warts. - Filiform Warts
Filiform warts are long, thin growths that appear on the face, particularly around the mouth, nose, or eyes. They are often caused by HPV types 1, 2, 4, and 27.
How Do Warts Spread?
Warts are highly contagious and spread through direct contact with HPV. This can occur when you touch a wart on your own body or come into contact with a surface that someone with warts has touched. The virus thrives in warm, moist environments, such as public swimming pools or locker rooms, which is why plantar warts are so common among swimmers and athletes. Additionally, HPV can spread through sexual contact, making genital warts a significant concern in sexually active populations.
It’s important to note that while warts are contagious, not everyone who comes into contact with HPV will develop them. Some individuals are more susceptible to the virus due to weakened immune systems or genetic factors.
Risk Factors for Developing Warts
While anyone can develop warts, certain factors increase your risk of contracting HPV and developing warts:
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV or those undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to warts.
- Age: Children and teenagers are more likely to develop common warts due to their frequent contact with other children and a less-developed immune system.
- Skin Injuries: Small cuts or breaks in the skin provide an entry point for the HPV virus, increasing the likelihood of developing warts.
- Frequent Use of Public Spaces: Using public showers, pools, or locker rooms can increase the risk of developing plantar warts due to the moist environment where HPV thrives.
Treatment Options for Warts
Warts often go away on their own as the body’s immune system fights off the HPV infection. However, this process can take months or even years. Many individuals seek treatment for warts due to their unsightly appearance or discomfort. Here are some of the most common treatment options:
- Over-the-Counter Treatments
Salicylic acid is one of the most common treatments for warts. It works by gradually removing the infected skin. These products are available in various forms, including gels, liquids, and adhesive pads. - Cryotherapy
This involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen. Cryotherapy causes the wart to blister and eventually fall off. While effective, it may require several sessions. - Cantharidin
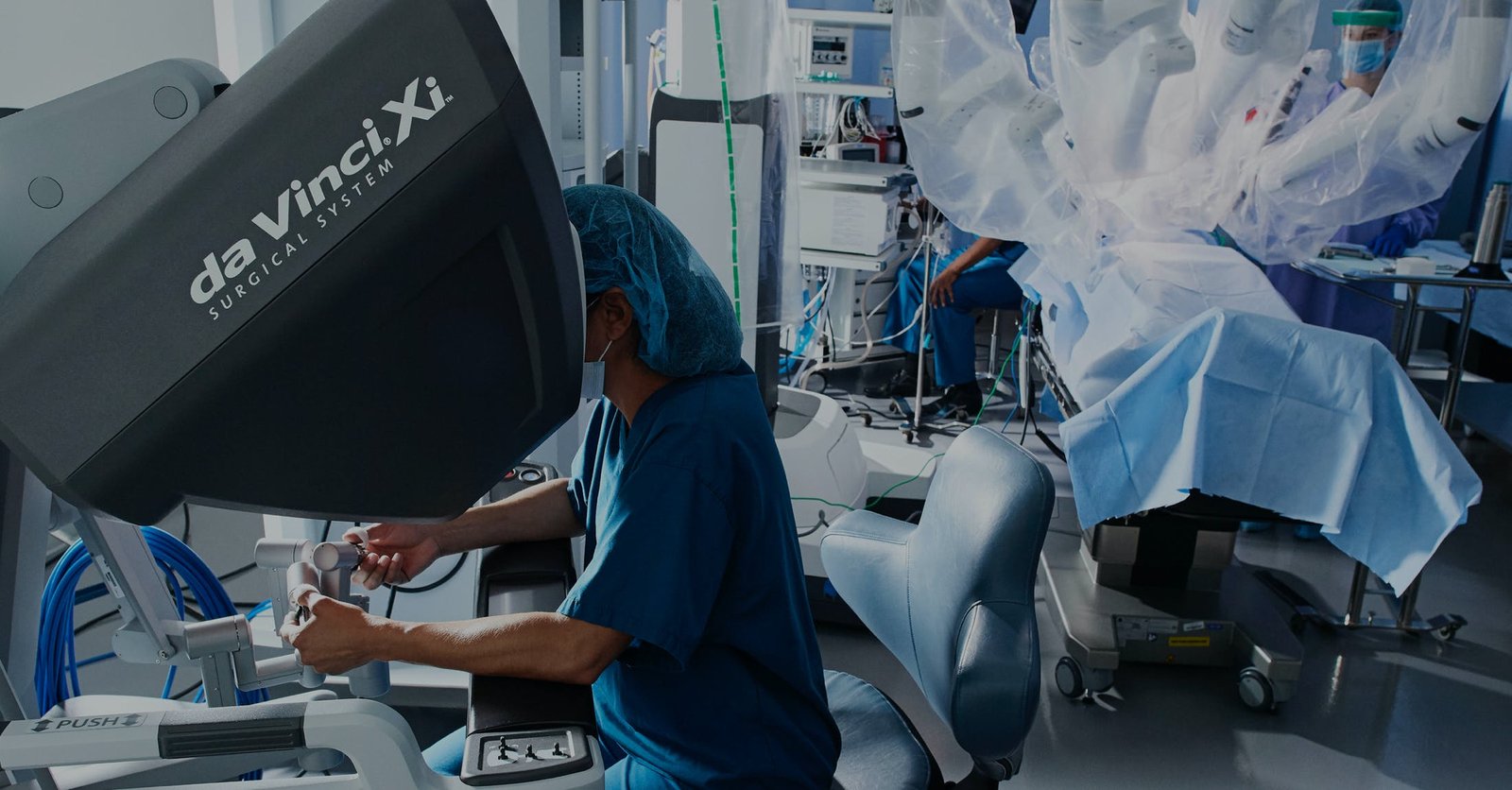
A healthcare provider may apply cantharidin, a substance that causes the wart to blister and peel off. - Laser Therapy
In more severe cases, a doctor may use a laser to burn off the wart. - Immune System Boosting Treatments
For individuals with persistent warts, treatments that stimulate the immune system to fight off the virus may be necessary. These include topical creams like imiquimod.
Preventing Warts
While warts are difficult to prevent entirely, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of contracting HPV and developing warts:
- Avoid Direct Contact with Warts: Refrain from touching warts on yourself or others.
- Keep Skin Clean and Dry: Moist skin is more susceptible to HPV. Always dry your skin thoroughly, particularly after being in a public place.
- Wear Foot Protection in Public Areas: Wearing sandals or shower shoes in public pools and locker rooms can reduce your risk of plantar warts.
- Avoid Biting Your Nails or Picking at Skin: Damaged skin provides an entry point for the HPV virus.
- Practice Safe Sex: Use protection during sexual activity to reduce the risk of contracting genital warts.
Conclusion: Stay Wart-Free with Preventative Care
While warts may seem like a minor nuisance, understanding their causes and how they spread is key to preventing them. With proper skin care, good hygiene, and awareness of the risk factors, you can reduce your chances of contracting HPV and developing warts. If you already have warts, rest assured that there are effective treatment options available to help you manage or eliminate them.
By staying proactive, you can take control of your skin health and minimize the impact of warts on your life.