Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, causing it to develop patches of thick, red, scaly skin. Though it can affect anyone, psoriasis is commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. It can be a physically and emotionally challenging condition, but with proper management, those affected can lead full and comfortable lives. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and best treatments available for psoriasis, with a focus on promoting healthier skin and improved well-being.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a long-lasting autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing them to multiply rapidly. Normally, skin cells regenerate every 28–30 days, but in people with psoriasis, new cells form within just a few days. This results in the buildup of dead skin cells on the surface, forming thick, flaky, silvery scales.
There are different types of psoriasis, each presenting unique symptoms, though all forms of the condition share the same underlying cause—an overactive immune system.
Types of Psoriasis
- Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris): This is the most common form, accounting for about 80-90% of cases. It causes red, inflamed patches covered with white or silver scales, often appearing on the elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Characterized by small, dot-like lesions, guttate psoriasis is usually triggered by bacterial infections such as strep throat. It is more common in children and young adults.
- Inverse Psoriasis: This type appears as smooth, red patches of skin in areas where skin folds, such as under the breasts, in the armpits, or around the groin.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Marked by white pustules (blisters of noninfectious pus) surrounded by red skin, pustular psoriasis can affect large or small areas of the body.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare but severe form, erythrodermic psoriasis can cover the entire body with a red, peeling rash that can cause intense itching and pain.
Causes of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is not entirely understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The immune system, specifically T cells, is responsible for fighting infections and diseases. In people with psoriasis, T cells mistakenly attack healthy skin cells, causing the rapid turnover that leads to the scaly patches characteristic of the condition.
Factors that can trigger or worsen psoriasis include:
- Genetics: About one-third of people with psoriasis have a family history of the condition. If one parent has psoriasis, there is a 10% chance their child will develop it. If both parents have it, that likelihood jumps to 50%.
- Stress: Emotional stress is a common trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or therapy can reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
- Infections: Infections like strep throat, bronchitis, or respiratory conditions can trigger guttate psoriasis or worsen existing conditions.
- Weather Conditions: Cold, dry weather often worsens psoriasis symptoms, while warm, humid climates can provide relief.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, and obesity are known to trigger and exacerbate psoriasis.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as lithium, beta-blockers, and antimalarials, may worsen psoriasis.
Symptoms of Psoriasis

Psoriasis symptoms vary depending on the type, but common signs include:
- Red patches of skin covered with silvery scales
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
- Itching, burning, or soreness
- Thickened or ridged nails
- Swollen and stiff joints (common in psoriatic arthritis)
The severity of psoriasis can range from mild, with small patches, to severe, covering large areas of the body. The condition can also affect mental well-being, as individuals may experience embarrassment, anxiety, or depression due to their appearance.
Psoriasis Treatment Options
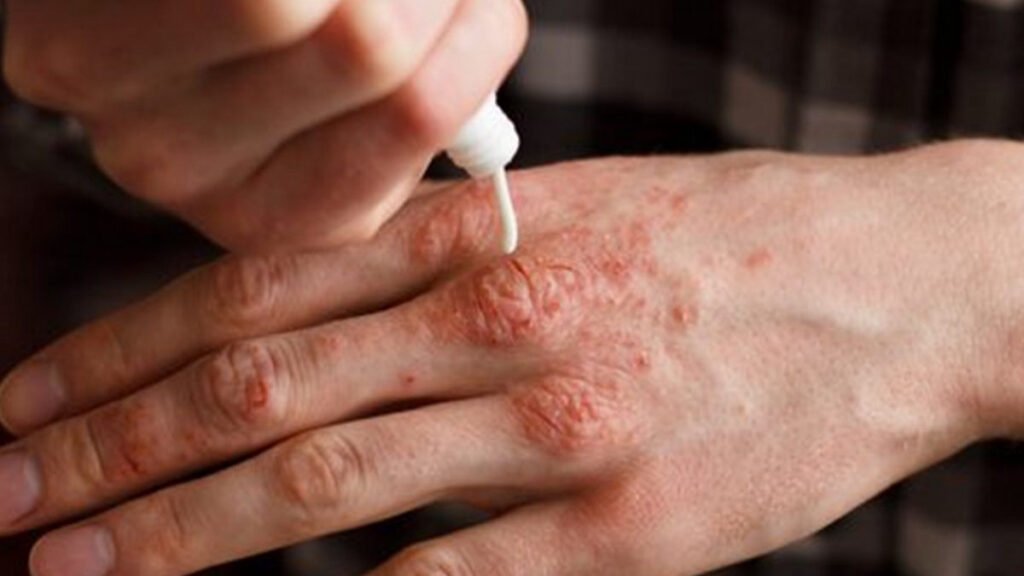
While there is no cure for psoriasis, treatments are available to reduce symptoms and control flare-ups. The goal is to slow the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation. Here are some of the most effective treatments available today:
1. Topical Treatments
For mild to moderate cases of psoriasis, topical treatments applied directly to the skin are often the first line of defense. These include:
- Corticosteroids: Anti-inflammatory creams that reduce swelling and redness.
- Vitamin D Analogues: These slow the growth of skin cells and can be used in combination with corticosteroids.
- Retinoids: Topical retinoids, derived from vitamin A, help slow skin cell production and reduce inflammation.
- Coal Tar: This traditional remedy helps reduce scaling, itching, and inflammation, though its strong odor and staining properties may be undesirable for some.
2. Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
Moderate to severe psoriasis may be treated with light therapy, where the skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. This can help slow skin cell turnover and reduce scaling.
- UVB Phototherapy: Exposure to UVB light reduces the growth of affected skin cells.
- PUVA Therapy: This treatment involves taking a medication called psoralen, which makes the skin more sensitive to light, followed by UVA exposure.
3. Systemic Treatments
For severe cases of psoriasis, oral or injectable medications may be necessary. These treatments work throughout the body to suppress the immune system and reduce symptoms.
- Methotrexate: This drug reduces the production of skin cells and is often used in severe psoriasis cases.
- Cyclosporine: A powerful immune-suppressing drug that can provide rapid relief but requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects.
- Biologics: These are newer, targeted therapies that work by blocking specific immune system molecules involved in the inflammation process.
4. Natural Remedies
Some individuals turn to natural remedies to alleviate symptoms. While they cannot replace medical treatment, remedies such as aloe vera, fish oil supplements, and oatmeal baths may help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.
Preventing Psoriasis Flare-ups
Preventing psoriasis flare-ups involves identifying and avoiding personal triggers. Here are some effective strategies to minimize outbreaks:
- Manage Stress: Since stress is a common trigger, it’s important to incorporate stress-relief practices such as yoga, meditation, or breathing exercises into your routine.
- Maintain Healthy Skin: Keeping your skin moisturized is crucial. Use thick creams or ointments to lock in moisture and avoid irritating soaps or fragrances.
- Protect Your Skin: In cold, dry weather, cover your skin to prevent it from drying out. Sunlight in moderation can be beneficial, but too much exposure can cause sunburn and exacerbate symptoms.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as both have been linked to psoriasis flare-ups. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can reduce the severity of symptoms.
Living with Psoriasis
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, but with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments, most people are able to manage their symptoms effectively. Support groups and counseling can be helpful for those struggling with the emotional impact of the condition. Regular check-ins with a dermatologist can help monitor the progression of psoriasis and make necessary adjustments to treatment.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a lifelong autoimmune condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Although there is no cure, advances in treatment have made it possible to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Understanding the causes, triggers, and treatment options for psoriasis is key to controlling the condition and reducing flare-ups. By working closely with healthcare providers and making lifestyle changes, individuals with psoriasis can lead fulfilling, healthy lives.
Scientific Sources:
- National Psoriasis Foundation: About Psoriasis
- Mayo Clinic: Psoriasis
- American Academy of Dermatology: Psoriasis: Overview
This article aims to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of psoriasis, helping readers navigate their treatment options while promoting healthy, confident living.