Lupus, specifically Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease that affects millions worldwide. This complex condition can be difficult to understand and manage, as it affects multiple organs and systems in the body. In this article, we will explore what lupus is, its symptoms, causes, and how to manage the disease to lead a healthy life.
What is Lupus?
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder, meaning that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues and organs. In the case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), the most common form of lupus, the inflammation can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, and brain. Because lupus symptoms mimic those of other diseases, it’s often called “the great imitator.”
Symptoms of Lupus
Lupus manifests differently from person to person, making it challenging to diagnose. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue: Persistent exhaustion, even after sufficient rest.
- Joint pain and swelling: Particularly in the hands, knees, and wrists.
- Skin rashes: A hallmark of lupus is the butterfly-shaped rash that appears on the face.
- Hair loss: Hair thinning or patchy bald spots.
- Fever: Unexplained fevers can occur frequently.
- Chest pain: Caused by inflammation of the heart or lungs.
- Kidney problems: Lupus nephritis can cause swelling in the legs and high blood pressure.
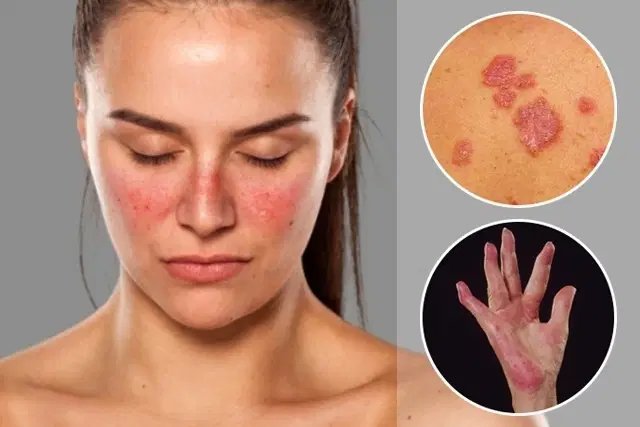
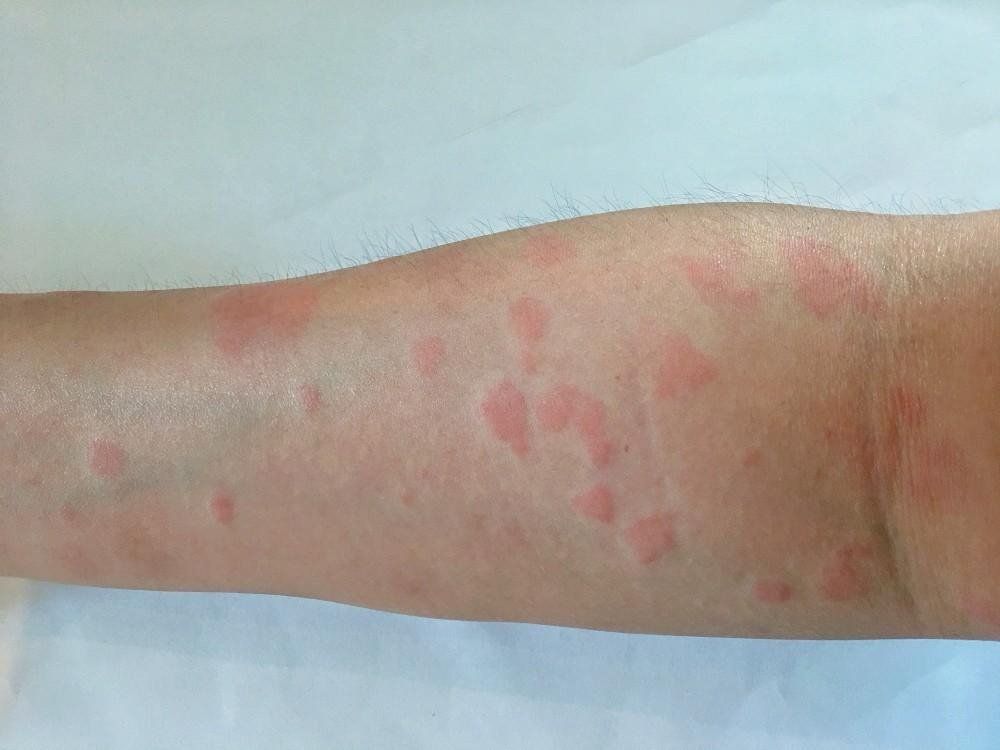
These symptoms can flare up unpredictably, with periods of remission followed by sudden exacerbations.
What Causes Lupus?
While the exact cause of lupus remains unknown, researchers believe a combination of genetic and environmental factors trigger the disease. Women, especially those of African, Hispanic, and Asian descent, are more likely to develop lupus. Some common triggers include:
- Infections: Viral infections can activate lupus in genetically predisposed individuals.
- Sunlight: Ultraviolet (UV) exposure can trigger lupus-related skin issues.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics and anti-seizure drugs, have been linked to drug-induced lupus.
- Hormonal changes: Lupus is more common in women of childbearing age, suggesting a link to estrogen.
Managing Lupus: Treatment and Lifestyle Tips
Although there is no cure for lupus, treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. A combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring by healthcare professionals can make a significant difference.
1. Medications
Lupus treatment often involves a range of medications, including:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Help reduce pain and inflammation in joints.
- Corticosteroids: Used to suppress the immune system and control flare-ups.
- Antimalarial drugs: These are effective in treating skin and joint symptoms.
- Immunosuppressants: Help to reduce the activity of the immune system, especially in severe cases of lupus affecting organs.
2. Lifestyle Adjustments
Making the right lifestyle changes can help manage lupus symptoms:
- Stay Active: Regular, low-impact exercise such as swimming or walking can help improve mobility and reduce fatigue.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3-rich fish, can support overall health.
- Protect Your Skin: Use sunscreen and protective clothing when outdoors, as UV exposure can worsen symptoms.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can lead to flare-ups. Practicing mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress levels.
3. Regular Medical Checkups
Frequent medical consultations are essential for lupus patients to monitor the progress of the disease and adjust treatments as needed. Blood tests, urine tests, and imaging scans are often used to check for internal organ damage.
Living with Lupus: What You Should Know
Living with lupus can be overwhelming, but with the right support system and management strategies, many people lead fulfilling lives. Education is key—learning as much as possible about lupus can help both patients and their families cope better with the disease.
Moreover, support groups provide an outlet for sharing experiences and gaining emotional support from others who understand the challenges of living with lupus. Maintaining a positive mindset and seeking help when needed are critical to managing this unpredictable condition.
Conclusion
Lupus (SLE) is a chronic condition that requires lifelong management, but with the right approach, flare-ups can be minimized, and quality of life can be improved. Early detection, regular medical checkups, and lifestyle adjustments are vital to keeping lupus under control. By staying informed and proactive, individuals with lupus can live healthier and more fulfilling lives.




