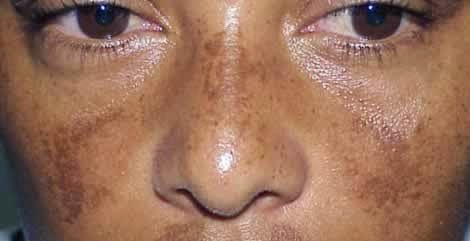
Skin pigmentation refers to the natural color of a person’s skin, determined by melanin, a pigment produced by melanocytes. However, various factors can lead to hyperpigmentation—darkened patches or spots that result in uneven skin tone. Hyperpigmentation can affect individuals of all skin types and is a common concern for many. In this article, we’ll explore the causes of skin pigmentation, available treatments, and preventive measures to help you achieve clear, even-toned skin.
What is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin due to the production of melanin. Melanin helps protect the skin from ultraviolet (UV) radiation and contributes to the skin’s overall appearance. However, when melanin production becomes imbalanced, it can lead to skin pigmentation issues, such as dark spots, patches, or even lighter areas on the skin.
Hyperpigmentation occurs when certain areas of the skin produce more melanin than usual, causing those areas to become darker than the surrounding skin. Conversely, hypopigmentation occurs when there is reduced melanin production, leading to lighter patches of skin.
Causes of Skin Pigmentation

Understanding the root causes of skin pigmentation is essential to finding the right treatment. Several factors contribute to changes in skin pigmentation, including:
1. Sun Exposure
Prolonged exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays is the most common cause of hyperpigmentation. UV rays stimulate the production of melanin, leading to the formation of sunspots or age spots, especially in areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and hands.
2. Hormonal Changes
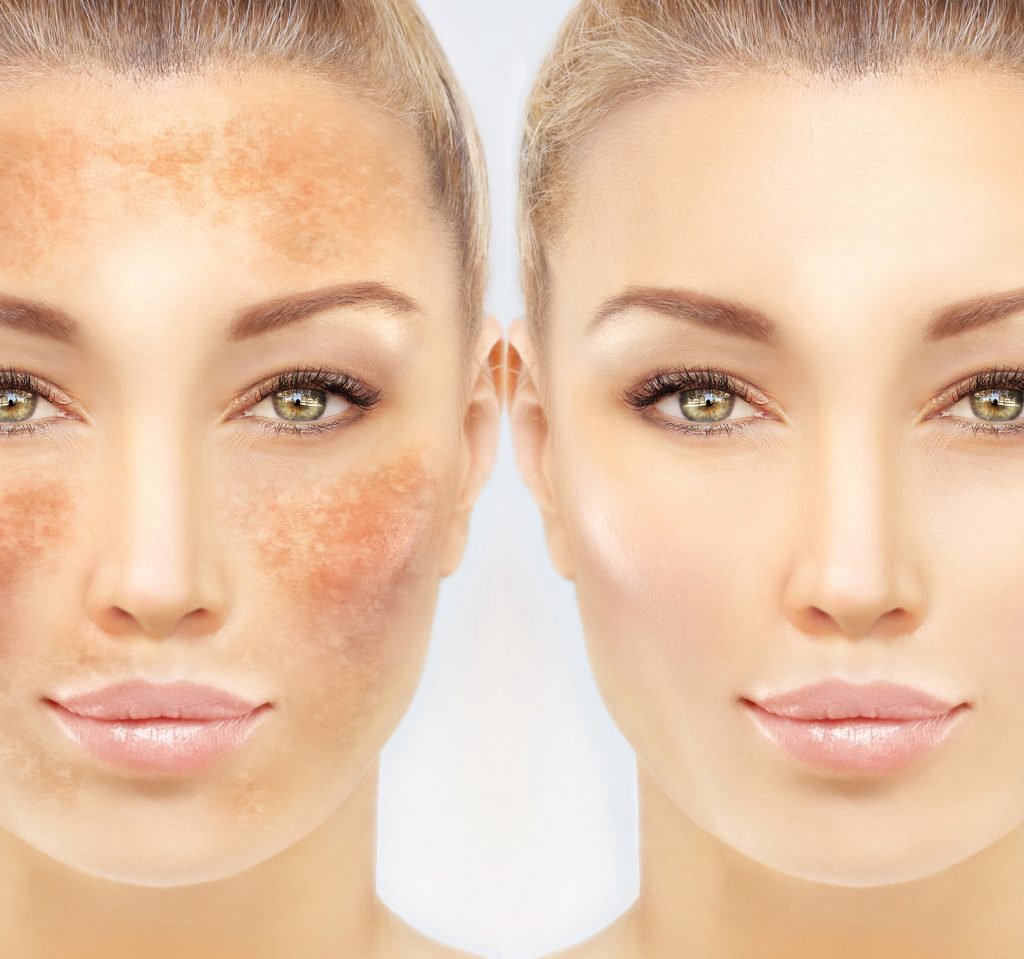
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills, can lead to a condition known as melasma, characterized by dark patches on the skin. Melasma is often triggered by both hormonal imbalances and sun exposure.
3. Inflammation and Injury
Inflammation caused by acne, eczema, or other skin conditions can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). This occurs when the skin heals after inflammation or injury, leaving behind dark marks or spots.
4. Aging
As we age, the skin naturally produces less collagen and becomes more susceptible to sun damage, which can lead to age spots or liver spots. These areas of hyperpigmentation are common in people over the age of 50 but can appear earlier due to prolonged sun exposure.
5. Genetics
In some cases, genetics play a role in skin pigmentation. Certain individuals may be predisposed to developing pigmentation issues, such as freckles, due to their genetic makeup.
6. Medications
Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, antibiotics, or anti-seizure medications, can lead to hyperpigmentation as a side effect. Additionally, topical treatments containing retinoids or hydroquinone may also lead to skin irritation, causing pigmentation issues.
Types of Skin Pigmentation
There are several types of skin pigmentation issues, each with its unique characteristics and causes:
1. Melasma
Melasma is characterized by dark, irregular patches on the skin, often caused by hormonal changes and sun exposure. It typically appears on the face, especially on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip.
2. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
PIH occurs when the skin darkens after inflammation or injury, such as after acne, cuts, or burns. The affected areas may range from pink to red to dark brown, depending on skin tone and the extent of the injury.
3. Solar Lentigines (Sunspots)
Sunspots, also known as age spots or liver spots, are dark patches that develop after prolonged exposure to the sun’s UV rays. They are more common in older individuals and appear on areas exposed to the sun, such as the hands, face, and shoulders.
4. Freckles
Freckles are small, brown spots that appear on sun-exposed areas, especially in fair-skinned individuals. While not harmful, they can darken and become more noticeable with increased sun exposure.
Effective Treatments for Skin Pigmentation
Fortunately, there are various treatments available to reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation and restore an even skin tone. Depending on the severity and type of pigmentation, a dermatologist may recommend different approaches:
1. Topical Treatments
Topical creams and serums containing ingredients such as hydroquinone, kojic acid, azelaic acid, vitamin C, and retinoids can help lighten dark spots and even out skin tone. These treatments work by inhibiting melanin production and promoting skin cell turnover.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the top layer and allows new, evenly pigmented skin to form. Chemical peels can be effective for treating sunspots, melasma, and PIH. Mild peels, such as glycolic acid, are commonly used, while stronger peels may be required for more severe pigmentation issues.
3. Laser Therapy
Laser treatments, such as fractional lasers or intense pulsed light (IPL), target and break down pigment cells in the skin. This treatment is effective for sunspots, melasma, and other pigmentation issues but should be performed by a skilled dermatologist to avoid potential side effects.
4. Microdermabrasion and Dermabrasion
Microdermabrasion involves gently exfoliating the top layer of the skin to reduce the appearance of pigmentation. Dermabrasion, on the other hand, is a more intense procedure that involves the removal of the outer layer of skin, which can help reduce deeper pigmentation issues.
5. Prescription Medications
In some cases, a dermatologist may prescribe oral or topical medications, such as tranexamic acid, to reduce melanin production and treat pigmentation disorders like melasma.
Preventing Skin Pigmentation
Prevention is key when it comes to avoiding pigmentation issues. Taking the necessary precautions can help maintain clear, even skin. Here are some steps to prevent hyperpigmentation:
1. Sun Protection
Wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every day is the most important step in preventing hyperpigmentation. Sunscreen should be applied to all exposed areas of the skin, even on cloudy days or indoors. Reapply every two hours when outdoors, and wear protective clothing such as hats and sunglasses.
2. Avoiding Tanning
Tanning beds and excessive sun exposure should be avoided to prevent melanin overproduction. Opt for self-tanning products if you want a sun-kissed glow without the risk of pigmentation.
3. Treating Skin Conditions Promptly
Addressing acne, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions promptly can help reduce the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Avoid picking at the skin, as this can worsen pigmentation.
4. Using Gentle Skincare Products
Choose skincare products that are gentle on the skin and free from harsh chemicals or fragrances that can cause irritation. Products containing niacinamide and antioxidants can help brighten the skin and prevent pigmentation issues.
5. Regular Exfoliation
Exfoliating the skin regularly can help remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover, reducing the risk of hyperpigmentation. Use gentle exfoliants such as alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) to avoid irritation.
Conclusion: Achieving Clear, Even Skin
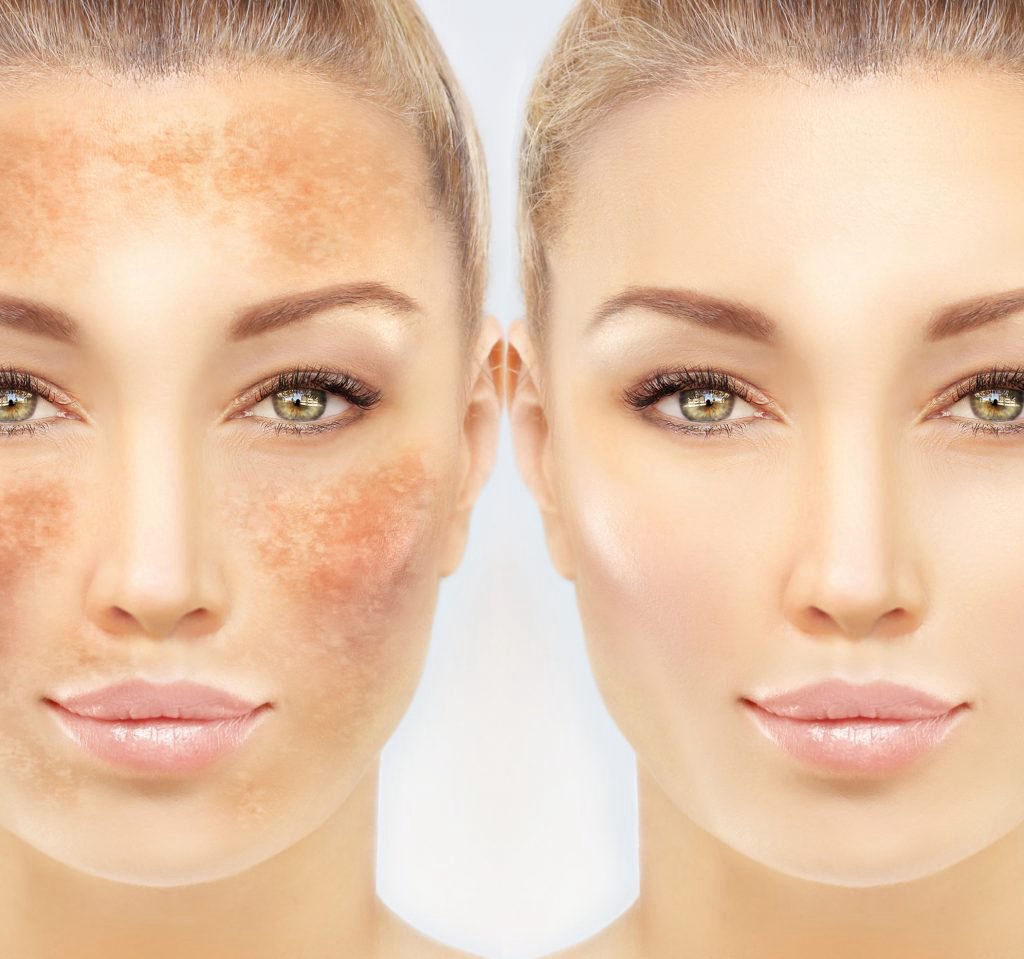

Hyperpigmentation is a common skin concern, but with the right approach, it can be effectively managed and treated. Whether caused by sun exposure, hormonal changes, or inflammation, understanding the root cause of pigmentation issues is key to finding the most appropriate treatment. By protecting the skin from UV damage, using targeted treatments, and following preventive measures, you can achieve clear, even-toned skin and improve overall skin health.
Scientific Sources:
- American Academy of Dermatology: Hyperpigmentation
- Mayo Clinic: Skin Pigmentation Disorders
- Cleveland Clinic: Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
- Harvard Health: Protecting Your Skin from the Sun
By addressing skin pigmentation concerns and taking steps to protect your skin, you can enjoy a radiant, even complexion.