Introduction: Understanding Varicocele and Its Effect on Male Fertility
Varicocele, also known as testicular varicose veins, is a condition that affects the veins in the scrotum and is a significant yet often overlooked cause of male infertility. It is estimated that 15% of men experience varicocele, and among infertile men, the prevalence rises to about 40%. Despite its commonality, many men remain unaware of this condition until they face difficulties in conceiving.
In this article, we will delve into what varicocele is, its symptoms, causes, and most importantly, the available treatment options. For men struggling with fertility, addressing varicocele could be the key to improving reproductive outcomes.
What Is Varicocele?
Varicocele is an enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, specifically in the pampiniform plexus, a network of veins responsible for cooling the blood before it reaches the testicles. This cooling is crucial for optimal sperm production. When the veins enlarge, blood pools in the scrotum, increasing the temperature around the testicles, which negatively impacts sperm production and function.
Causes of Varicocele
The primary cause of varicocele is the malfunctioning of the valves in the veins of the scrotum. Normally, these valves regulate blood flow to and from the testicles. When the valves fail, blood pools in the veins, leading to the dilation of the veins. This condition is more common on the left side of the scrotum due to the anatomical layout of the male body.
Several factors contribute to the development of varicocele, including:
1. Genetics: A family history of varicose veins increases the risk of developing varicocele.
2. Body Composition: Overweight men or those with poor circulation may be more prone to developing this condition.
3. Physical Activity: Strenuous physical activity or heavy lifting can contribute to the formation of varicocele.
Symptoms of Varicocele
In many cases, varicocele produces no symptoms, making it difficult to detect without a medical examination. However, in some cases, men may experience:
• A dull, aching pain in the scrotum
• Swelling or lump in the testicle
• Noticeable enlargement of veins in the scrotum (feels like a “bag of worms”)
• Testicular discomfort, especially after physical activity or standing for long periods
• Fertility problems or difficulty conceiving
How Varicocele Affects Male Fertility
Varicocele has a direct impact on male fertility due to the increase in scrotal temperature, which disrupts normal sperm production. Studies show that varicocele can lead to:
• Decreased sperm count: Fewer sperm cells are produced.
• Poor sperm quality: Sperm morphology (shape) and motility (ability to swim) may be affected.
• Hormonal imbalances: Varicocele can lower testosterone levels, further impairing reproductive function.
In addition to these factors, varicocele can cause oxidative stress, which damages sperm DNA. Without treatment, this condition can continue to deteriorate sperm quality and lead to long-term fertility issues.
Treatment Options for Varicocele
Several treatment options are available for men diagnosed with varicocele. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and its impact on fertility. Here are the most common treatments:
1. Microsurgical Varicocelectomy
Microsurgical varicocelectomy is the most effective and widely recommended treatment for varicocele. This procedure involves tying off the affected veins through a small incision in the groin or abdomen. It is minimally invasive and has a high success rate, with most patients seeing an improvement in sperm parameters and fertility post-surgery. Recovery time is short, and complications are rare.
2. Varicocele Embolization
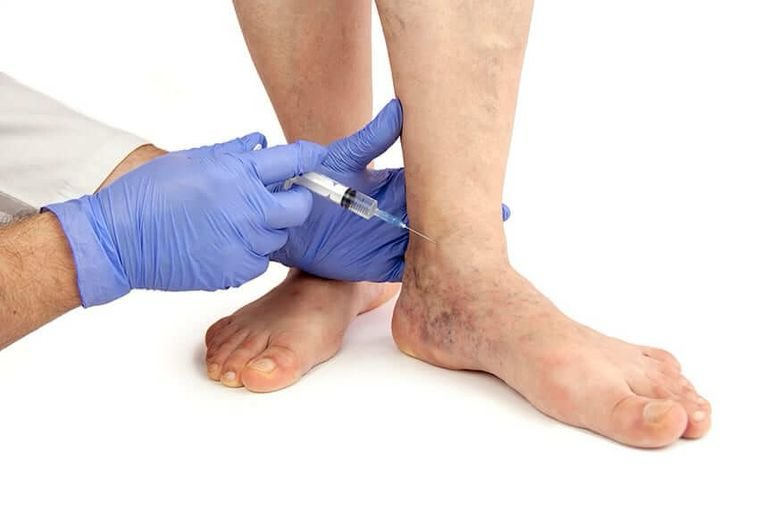
Varicocele embolization is a non-surgical, minimally invasive treatment where a small catheter is inserted into a vein in the groin. A coil or liquid substance is then used to block the abnormal veins, redirecting blood flow away from the affected area. Embolization is an excellent option for men seeking a non-surgical alternative, with comparable success rates to varicocelectomy.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
In some cases, making certain lifestyle changes may help alleviate the symptoms of varicocele, especially in mild cases. These changes include:
• Wearing supportive underwear: This can help relieve discomfort by providing extra support.
• Avoiding heavy lifting: Reducing strain on the body can minimize symptoms.
• Maintaining a healthy weight: A healthy BMI can improve overall circulation and reduce pressure on the veins.
• Avoiding excessive heat: Staying away from saunas, hot tubs, and other heat sources that can raise scrotal temperature.
While these changes alone may not cure varicocele, they can help manage discomfort and improve sperm health.
Can Varicocele Be Prevented?
Unfortunately, there is no known way to prevent varicocele, as it is largely due to anatomical factors. However, men who are diagnosed early and treated promptly can significantly reduce their risk of infertility. Regular check-ups and early intervention are crucial for maintaining reproductive health, especially for men experiencing symptoms like scrotal discomfort or issues with fertility.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you suspect you have varicocele, especially if you’re experiencing symptoms like pain, swelling, or difficulty conceiving, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider. Early detection and treatment can help prevent further complications, such as testicular atrophy (shrinking of the testicles) and ongoing fertility problems.
Conclusion: Don’t Let Varicocele Compromise Your Fertility
Varicocele is a common and treatable condition that can significantly impact male fertility. For men facing fertility issues, addressing varicocele through surgery, embolization, or lifestyle changes can dramatically improve sperm quality and increase the chances of conception. If you are struggling with fertility, speak to your doctor about testing for varicocele—early treatment could be the key to achieving your family goals.
Scientific Sources:
1. National Institutes of Health (NIH): Varicocele and Its Impact on Male Fertility
2. Mayo Clinic: Varicocele – Symptoms and Causes
3. American Urological Association: Varicocele and Fertility Treatment
4. Cleveland Clinic: Varicocele – Overview and Treatment Options